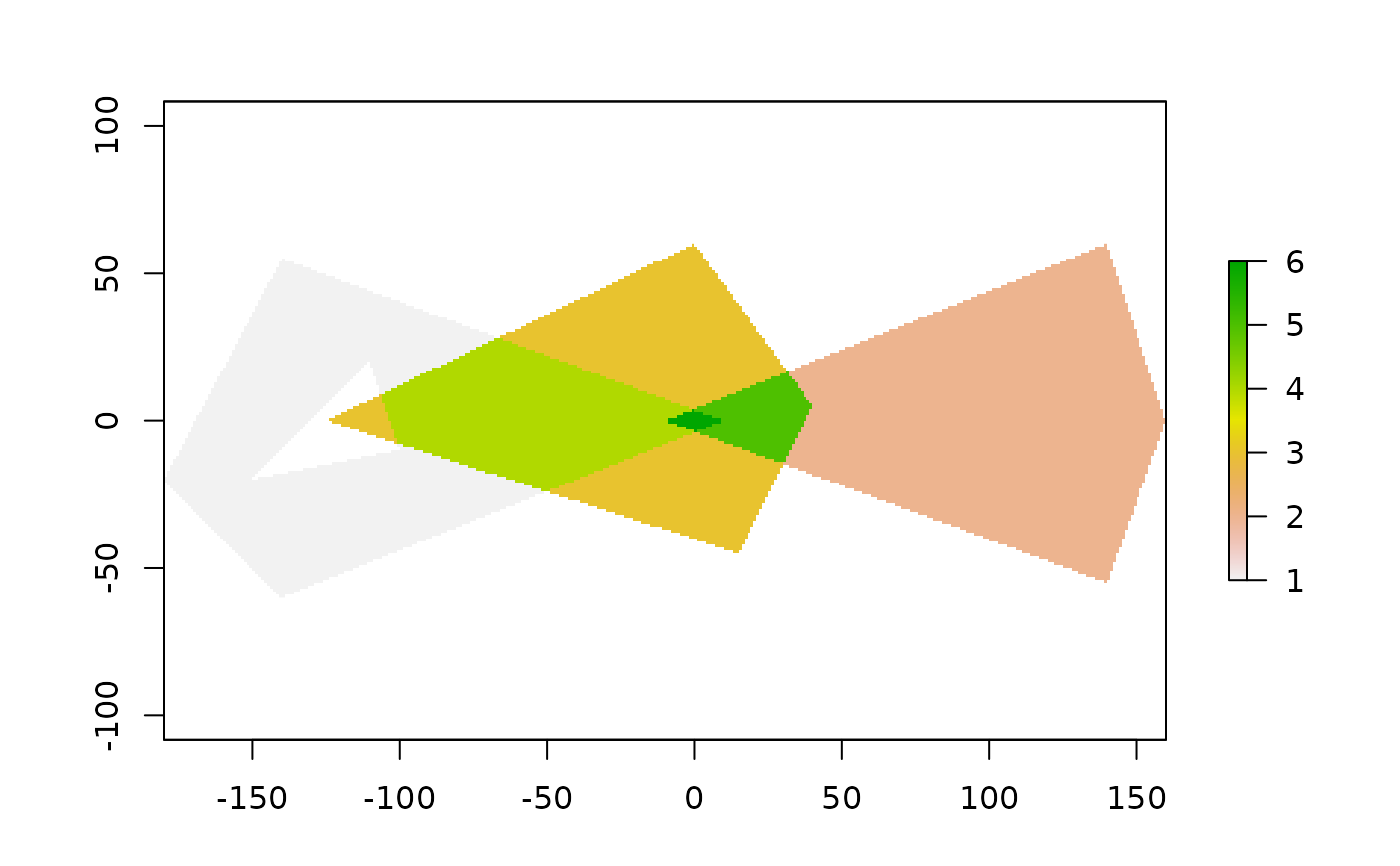
Rasterize set of polygons
fasterize(
sf,
raster,
field = NULL,
fun = "last",
background = NA_real_,
by = NULL
)Arguments
- sf
a polygon vector or data frame object with a geometry column of POLYGON and/or MULTIPOLYGON (equivalent) objects.
- raster
A raster object. Used as a template for the raster output. Can be created with
raster::raster(). The fasterize package provides a method to create a raster object from an polygon dataset.- field
character (or numeric vector). The name of a column in
sf, providing a value for each of the polygons rasterized. If NULL (default), all polygons will be given a value of 1. If a numeric vector this value will be used as the value given to the pixel. (No recycling is done).- fun
character. The name of a function by which to combine overlapping polygons. Currently takes "sum", "first", "last", "min", "max", "count", or "any". Future versions may include more functions or the ability to pass custom R/C++ functions. If you need to summarize by a different function, use
by=to get a RasterBrick and thenraster::stackApply()orraster::calc()to summarize.- background
numeric. Value to put in the cells that are not covered by any of the features of x. Default is NA.
- by
character. The name of a column in
sfby which to aggregate layers. If set, fasterize will return a RasterBrick with as many layers as unique values of thebycolumn.
Value
A raster of the same size, extent, resolution and projection as the provided raster template.
Details
This is a high-performance replacement for raster::rasterize().
The algorithm is based on the method described in course materials provided by Wayne O. Cochran. The algorithm is originally attributed to Wylie et al. (1967) doi:10.1145/1465611.1465619 .
Note that original implementation worked only for sf dataframes of class "sf", but this now works for any polygon vector (sfc, wkt, wkb, geos) or dataframe with a polygon vector supported by the wk package handlers.
References
Wylie, C., Romney, G., Evans, D., & Erdahl, A. (1967). Half-tone perspective drawings by computer. Proceedings of the November 14-16, 1967, Fall Joint Computer Conference. AFIPS '67 (Fall). doi:10.1145/1465611.1465619
Examples
library(wk)
library(fasterize)
p123 <- c(paste0("POLYGON ((-180 -20, -140 55, 10 0, -140 -60, -180 -20),",
"(-150 -20, -100 -10, -110 20, -150 -20))"),
"POLYGON ((-10 0, 140 60, 160 0, 140 -55, -10 0))",
"POLYGON ((-125 0, 0 60, 40 5, 15 -45, -125 0))")
pols <- data.frame(value = seq_along(p123), geometry = wk::as_wkt(p123))
ex <- as.numeric(wk_bbox(pols))[c(1, 3, 2, 4)]
r <- raster::raster(raster::extent(ex), res = 1)
r <- fasterize(pols, r, field = "value", fun="sum")
plot(r)